Defining Makeup Prosthetics Makeup
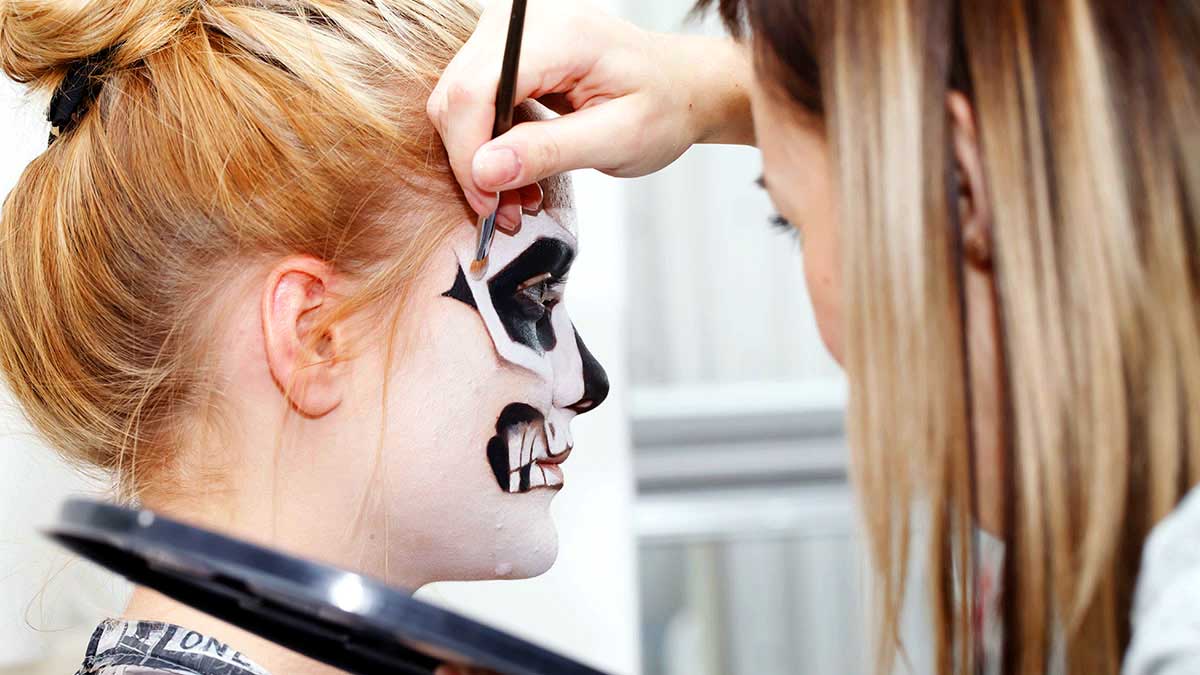
Makeup prosthetics, also known as special effects (SFX) makeup, is a field that combines artistic creativity with scientific precision to transform actors and characters in film, television, theater, and beyond. This discipline involves the creation and application of prosthetic body parts, enhancing or altering an individual’s appearance to meet specific artistic needs.
Relevance and Importance Prosthetics
The importance of makeup prosthetics cannot be overstated in the entertainment industry. From creating believable monsters and creatures to aging actors realistically or depicting injuries and other physical transformations, makeup prosthetics play a crucial role in storytelling. Their impact extends beyond entertainment, influencing fields such as medical training, education, and even psychological studies on perception and identity.
Historical Development
Early Beginnings
The history of makeup prosthetics dates back to ancient civilizations where rudimentary methods were used for religious and theatrical purposes. The Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all had their versions of makeup to depict gods, mythical creatures, and enhance dramatic performances.
Evolution Through the Ages
The 20th century saw significant advancements in prosthetic techniques with the rise of Hollywood. Pioneers like Lon Chaney and Jack Pierce revolutionized the field with groundbreaking work in films like “The Phantom of the Opera” and “Frankenstein”. The 1970s and 1980s further propelled the art with movies such as “Star Wars” and “The Exorcist,” showcasing complex and realistic designs.
Modern Innovations
Today, makeup prosthetics benefit from advanced materials and digital technologies. Silicone and 3D printing have transformed the industry, enabling more precise and lifelike creations. The integration of CGI with practical effects has opened new avenues for creators to push the boundaries of what’s possible on screen.
Key Techniques and Tools
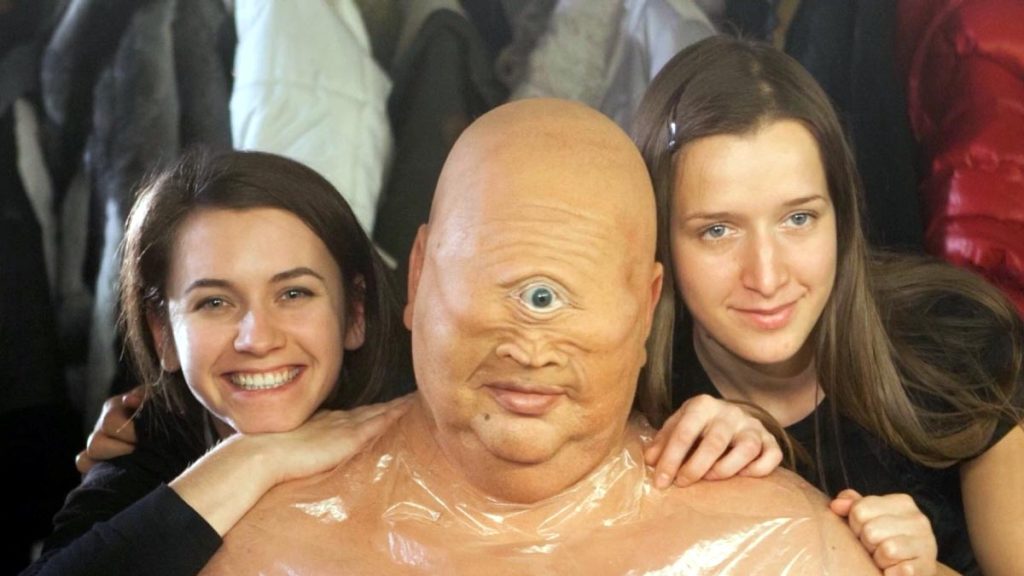

Sculpting and Mold Making
Creating prosthetics begins with sculpting, where artists design the desired look using clay or digital tools. Molds are then made from these sculptures to produce the prosthetic appliances. Materials like silicone, latex, and foam latex are commonly used, each chosen based on the needs of the specific application.
Application and Painting
Once the prosthetics are crafted, they are applied to the actor using medical-grade adhesives. The application process is intricate, requiring careful blending with the actor’s skin to achieve a seamless appearance. Painting and detailing are critical stages, adding realism through color, texture, and finishing touches.
Animatronics and Robotics
For more complex prosthetic creations, animatronics and robotics are employed. These technologies bring prosthetics to life, allowing movement and expression. This is particularly useful for creating lifelike creatures or enhancing human performances with mechanical enhancements.
Types and Categories of Prosthetics Makeup
Character Prosthetics
Used primarily in film and theater, character prosthetics transform actors into otherworldly beings or alter their appearance drastically. Examples include the transformations seen in “The Lord of the Rings” series or “Game of Thrones”.
Injury Simulation
Medical and military training often use prosthetic makeup to simulate injuries for educational purposes. These prosthetics provide realistic depictions of wounds, burns, and other trauma, aiding in effective training scenarios.
Cosmetic and Corrective Prosthetics
Beyond entertainment, prosthetics are also used for cosmetic purposes to correct physical deformities or injuries. These applications can dramatically improve the quality of life for individuals requiring such interventions.
Applications in Various Industries
Film and Television
The primary domain for makeup prosthetics, where it enhances storytelling by transforming actors into believable characters, be it fantastical creatures, historical figures, or futuristic beings.
Theater and Live Performances
Prosthetics in theater must withstand the rigors of live performance while ensuring visibility and comfort for the actors. This category includes masks, body suits, and other wearable prosthetics.
Medical Field
In medical training, prosthetics are essential for creating realistic simulations of injuries and diseases. This aids in practical training for medical professionals, enhancing their readiness for real-world scenarios.
Fashion and Art
Prosthetics have found a niche in fashion and art, where they are used to create avant-garde looks for runways, photo shoots, and installations. This application pushes the boundaries of conventional beauty and artistic expression.
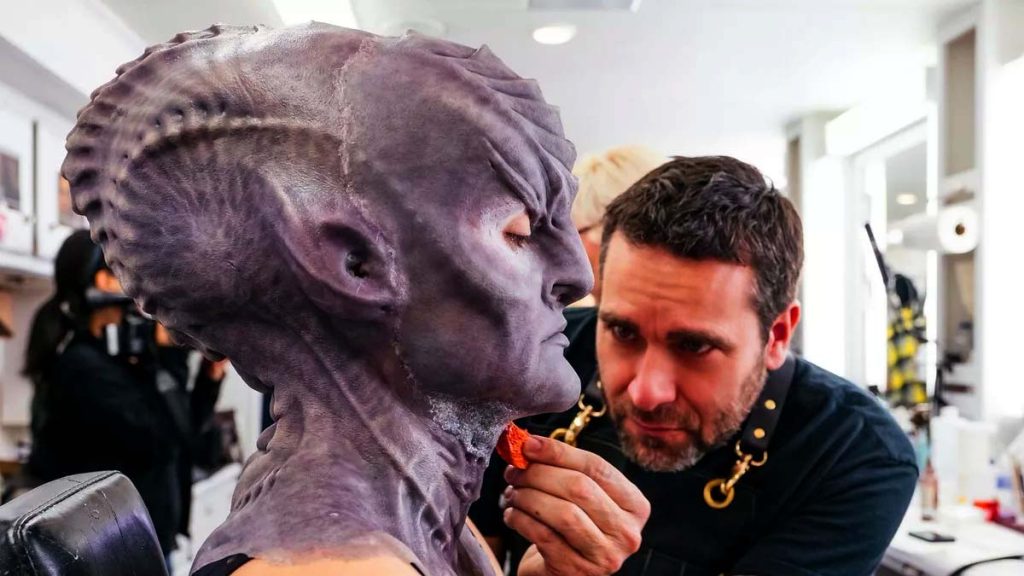

Benefits and Importance of Makeup Prosthetics
Enhancing Realism
Makeup prosthetics enhance the realism of characters and scenarios, making stories more believable and immersive for audiences.
Versatility and Creativity
The field allows for immense creativity and versatility, enabling artists to bring virtually any concept to life, from mythical creatures to futuristic visions.
Educational Value
In education, prosthetics provide invaluable tools for realistic training in medical and emergency response fields, enhancing learning and preparedness.
Challenges and Limitations
Time-Consuming Process
Creating and applying prosthetics is a time-intensive process, often requiring hours of meticulous work. This can be a limitation in productions with tight schedules.
Physical Comfort and Safety
Ensuring the comfort and safety of actors wearing prosthetics is paramount. Prolonged wear can cause discomfort or allergic reactions, necessitating careful material selection and application methods.
Cost Factors
High-quality prosthetics can be expensive, limiting their use in smaller budget productions. The cost of materials, skilled labor, and time all contribute to the overall expense.
Recent Innovations
Digital Integration
The integration of digital technology with traditional prosthetics has opened new possibilities. CGI and practical effects are now combined to achieve even more realistic results, as seen in recent blockbusters.
Advanced Materials
The development of new materials like silicone and advanced foam latex has improved the realism and durability of prosthetics. These materials offer better skin-like qualities and flexibility.
3D Printing
3D printing technology has revolutionized prosthetics, allowing for precise and customizable designs. This innovation speeds up the creation process and enhances the accuracy of the final product.
Future Prospects
Increased Realism
As materials and technologies continue to advance, the realism of prosthetics will only improve. Future developments may include smart materials that respond to environmental conditions or integrate with digital interfaces.
Broader Applications
Beyond entertainment, prosthetics will find expanded use in medical, educational, and even everyday applications, such as customizable wearables for cosmetic enhancement.
Environmental Sustainability
Future innovations will likely focus on sustainable materials and practices, reducing the environmental impact of prosthetic production and disposal.
Expert Insights
Industry Professionals
Quotes and advice from leading professionals in the field, such as Rick Baker or Stan Winston, provide valuable insights into the art and science of makeup prosthetics. Their experiences and innovations have shaped the industry and continue to inspire future generations.
Educational Institutions
Insights from institutions like the Cinema Makeup School or the Tom Savini Special Makeup Effects Program offer perspectives on the training and development of new talent in the field.
Final Wording
Makeup prosthetics is a dynamic and evolving field that blends artistic creativity with scientific precision. Its applications span entertainment, education, and beyond, enhancing realism and storytelling in various domains.